Due to the uncertainty and fuzziness of information, the traditional clustering analysis method sometimes cannot meet the requirement in practice. The clustering method based on intuitionistic fuzzy set has attracted more and more scholars attention nowadays. This paper discusses the intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm. There are a number of clustering techniques developed in the past using different distance/similarity measure. In this paper, we proposed a improved edge density minimal spanning tree initilization method using LINEX hellinger distance based weighted LINEX intuitionistic fuzzy c means clustering. IFCM considered an uncertainty parameter called hesitation degree and incorporated a new objective function which is based upon intutionistic fuzzy entropy in the conventional Fuzzy C-means. The clustering algorithm has membership and non membership degrees as intervals. Information regarding membership and typicality degrees of samples to all clusters is given by algorithm. Furthermore, the algorithm is extended for calculating membership and updating prototypes by minimizing the new objective function of weighted LINEX intuitionistic fuzzy c-means. Finally, the developed algorithms are illustrated through conducting experiments on random dataset, partition coefficient and validation function are used to evaluate the validity of clustering also this paper compares the results of proposed method with the results of existing basic intuitionistic fuzzy c-means.
| Published in | Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (Volume 12, Issue 2) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.jeee.20241202.12 |
| Page(s) | 36-47 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Science Publishing Group |
Intuitionistic Fuzzy C-means, Edge Density, Minimal Spanning Tree, Hellinger Distance, LINEX Function
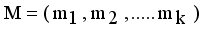 and
and 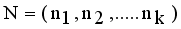 . Then Hellinger distance will be
. Then Hellinger distance will be 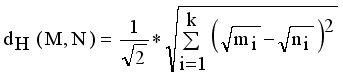
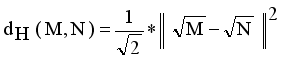
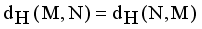 . Compared to other distance metrices, such as Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence ot total variation distance, Hellinger distance is more robust to outliers and in certain cases more accessible to compute. It finds widespread application in probability distribution comparisons and model fitting.
. Compared to other distance metrices, such as Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence ot total variation distance, Hellinger distance is more robust to outliers and in certain cases more accessible to compute. It finds widespread application in probability distribution comparisons and model fitting. 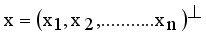 and
and 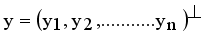 are two points of a MST and
are two points of a MST and 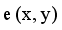 is an edge between x and y then LINEX Hellinger distance function between x and y is denoted by
is an edge between x and y then LINEX Hellinger distance function between x and y is denoted by 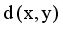 and calculated using equation (1)
and calculated using equation (1) 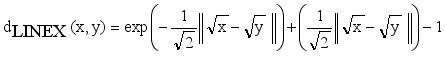 (1)
(1) 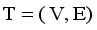 is the minimum spanning tree generated from dataset X of size N, where
is the minimum spanning tree generated from dataset X of size N, where 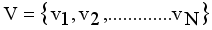 are vertices corresponding to objects,
are vertices corresponding to objects, 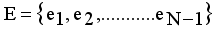 are edges corresponding to connection relationship between objects.
are edges corresponding to connection relationship between objects. 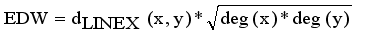 (2)
(2) 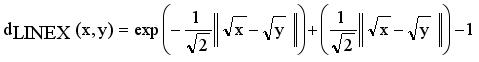 ,
, 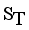 be the set of disjoint subtrees of LINEX measure MST.
be the set of disjoint subtrees of LINEX measure MST. 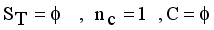
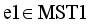 .
. 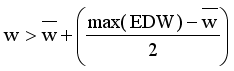 from MST
from MST 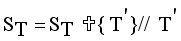 is new disjoint subtrees (regions).
is new disjoint subtrees (regions). 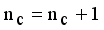 .
. 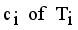 using average of points.
using average of points. 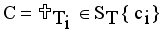 .
. 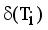 = Minimum standard deviation of edge density
= Minimum standard deviation of edge density 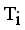 .
. 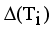 = Maximum standard deviation of edge density
= Maximum standard deviation of edge density 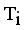 .
. 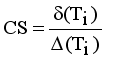
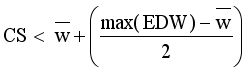
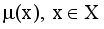 and non-membership
and non-membership 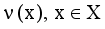 . An intuitionistic fuzzy set A in X, is written as
. An intuitionistic fuzzy set A in X, is written as 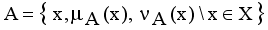
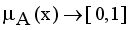 ,
, 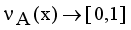 are the membership and non-membership degrees of an element in the set A with the condition
are the membership and non-membership degrees of an element in the set A with the condition 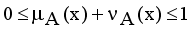 when
when 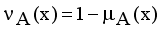 for every x in the set A, then the set A becomes a fuzzy set. Also indicated a hesitation degree,
for every x in the set A, then the set A becomes a fuzzy set. Also indicated a hesitation degree, 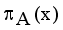 which arises due to lack of knowledge in defining the membership degree of each element x in the set A and is given by
which arises due to lack of knowledge in defining the membership degree of each element x in the set A and is given by 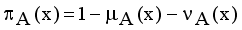 ,
, 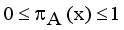
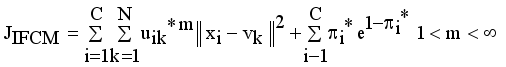 (3)
(3) 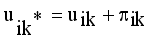 , where
, where 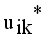 denotes the intuitionistic fuzzy membership and
denotes the intuitionistic fuzzy membership and 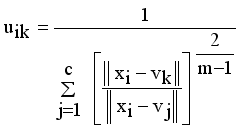 (4)
(4) 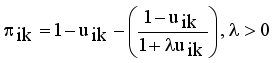 (5)
(5) 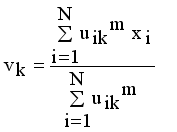 (6)
(6) 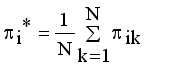 (7)
(7) 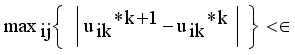 ,
, 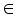 is a termination criterion between 0 and 1, where as k is the iteration steps. This procedure converges to a local minimum or a saddle point of
is a termination criterion between 0 and 1, where as k is the iteration steps. This procedure converges to a local minimum or a saddle point of 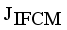 .
. 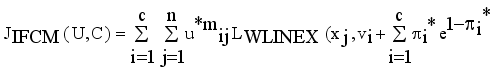
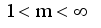 (8)
(8) 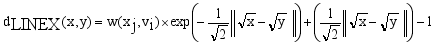
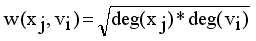
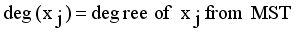 and
and 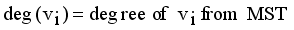
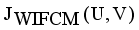 with constraint conditions
with constraint conditions 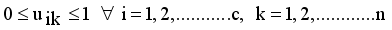
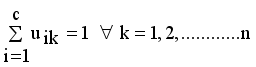 .
. 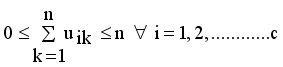
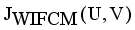 it is sufficient to minimize the following inner sum for fixed k:
it is sufficient to minimize the following inner sum for fixed k: 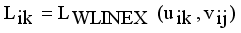
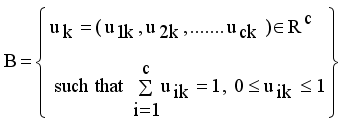
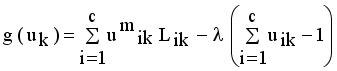
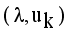 is stationary for F only if
is stationary for F only if 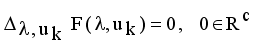 that yields to
that yields to 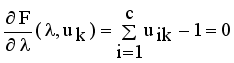 (9)
(9) 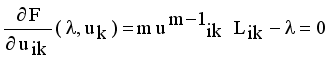 (10)
(10) 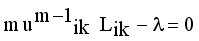
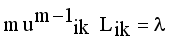
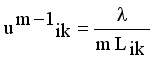
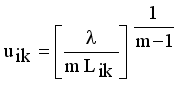
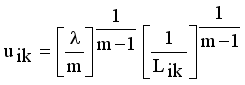 (11)
(11) 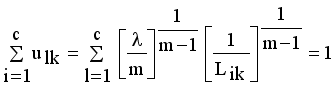
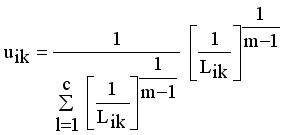
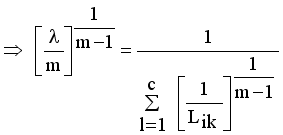 (12)
(12) 
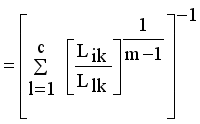
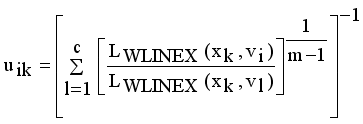 (13)
(13) 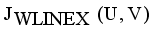 it is sufficient to minimize the following inner sum for fixed i:
it is sufficient to minimize the following inner sum for fixed i: 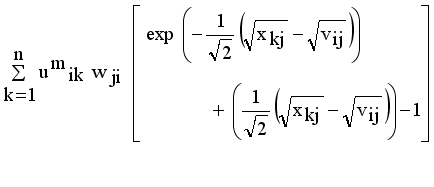
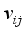 and setting the result to zero, we have the general form of updating center as
and setting the result to zero, we have the general form of updating center as 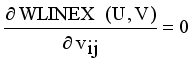
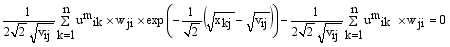
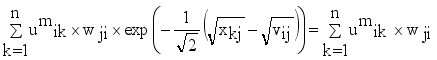
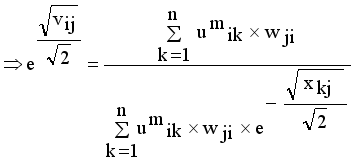
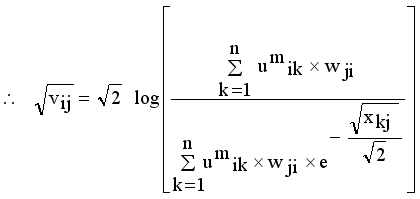
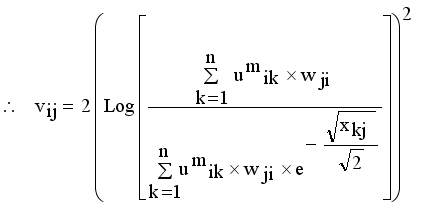 (14)
(14) 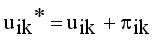 , where
, where 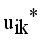 denotes the intuitionistic fuzzy membership and
denotes the intuitionistic fuzzy membership and 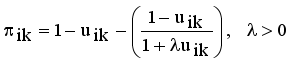 (15)
(15) 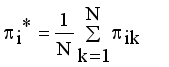 (16)
(16) 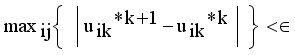
 by continuous updating
by continuous updating 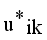 and
and 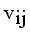 until the difference in successive
until the difference in successive 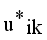 values is very small
values is very small 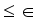 , where
, where 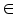 is a small positive value between 0 and 1.
is a small positive value between 0 and 1. 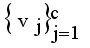 by using
by using 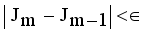 , where m is the iteration count,
, where m is the iteration count, 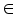 is a small number that can be set by the user.
is a small number that can be set by the user. 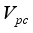 and Validation function
and Validation function 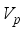 are used to evaluate the validity of clustering
are used to evaluate the validity of clustering 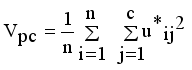 (17)
(17) 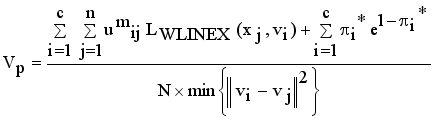 (18)
(18) Data | Intensity | Data | Intensity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
S. No | X | Y | I (v) | S. No | X | Y | I (v) |
1 | 2.50 | 3.00 | 0.75 | 11 | 15.80 | 20.50 | 0.25 |
2 | 3.80 | 3.50 | 0.50 | 12 | 11.80 | 12.50 | 0.35 |
3 | 7.00 | 1.80 | 0.15 | 13 | 15.50 | 14.50 | 0.80 |
4 | 3.10 | 4.80 | 0.18 | 14 | 5.50 | 10.50 | 0.70 |
5 | 5.50 | 7.50 | 0.45 | 15 | 18.50 | 19.50 | 0.40 |
6 | 8.50 | 9.50 | 0.75 | 16 | 12.50 | 13.80 | 0.25 |
7 | 10.80 | 11.50 | 0.60 | 17 | 21.80 | 12.50 | 0.95 |
8 | 4.20 | 3.80 | 0.25 | 18 | 19.80 | 20.50 | 0.25 |
9 | 2.80 | 1.80 | 0.45 | 19 | 19.00 | 20.00 | 0.60 |
10 | 12.50 | 20.50 | 0.65 | 20 | 11.00 | 12.00 | 0.30 |
S. No | Co-ordinate | intensity | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
x | y | I (v) | vertex | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
1 | 2.50 | 3.00 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.0000 | 0.0408 | 0.2892 | 0.0942 | 0.3091 | 0.6035 | 0.8693 | 0.0867 | 0.0449 | 1.5020 |
2 | 3.80 | 3.50 | 0.50 | 2 | 0.0000 | 0.1761 | 0.0490 | 0.1841 | 0.4338 | 0.6711 | 0.0140 | 0.0780 | 1.3012 | |
3 | 7.00 | 1.80 | 0.15 | 3 | 0.0000 | 0.2876 | 0.3871 | 0.5657 | 0.7566 | 0.1521 | 0.2048 | 1.4524 | ||
4 | 3.10 | 4.80 | 0.18 | 4 | 0.0000 | 0.1455 | 0.4181 | 0.6427 | 0.0337 | 0.1618 | 1.2158 | |||
5 | 5.50 | 7.50 | 0.45 | 5 | 0.0000 | 0.1029 | 0.2566 | 0.1525 | 0.4303 | 0.7407 | ||||
6 | 8.50 | 9.50 | 0.75 | 6 | 0.0000 | 0.0539 | 0.3941 | 0.7374 | 0.4416 | |||||
7 | 10.80 | 11.50 | 0.60 | 7 | 0.0000 | 0.6146 | 1.0036 | 0.2621 | ||||||
8 | 4.20 | 3.80 | 0.25 | 8 | 0.0000 | 0.1144 | 1.2360 | |||||||
9 | 2.80 | 1.80 | 0.45 | 9 | 0.0000 | 1.6847 | ||||||||
10 | 12.50 | 20.50 | 0.65 | 10 | 0.0000 | |||||||||
S. No | Edges | LINEX HELLINGER distance | S. No | Edges | LINEX HELLINGER distance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | (1, 2) | 0.0408 | 11 | (20, 12) | 0.0051 |
2 | (2, 8) | 0.0140 | 12 | (12, 16) | 0.0120 |
3 | (8, 4) | 0.0337 | 13 | (16, 13) | 0.0714 |
4 | (8, ) | 0.1144 | 14 | (13, 15) | 0.1204 |
5 | (8, 3) | 0.1521 | 15 | (15, 19) | 0.0064 |
6 | (8, 5) | 0.1525 | 16 | (15, 18) | 0.0124 |
7 | (5, 14) | 0.0619 | 17 | (15, 11) | 0.0313 |
8 | (14, 6) | 0.0767 | 18 | (11, 10) | 0.0635 |
9 | (6, 7) | 0.0539 | 19 | (11, 17) | 0.3183 |
10 | (7, 20) | 0.0136 |
S. No | Degree of MST | S. No | Degree of MST |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | 1 | 11 | 3 |
2 | 2 | 12 | 2 |
3 | 1 | 13 | 2 |
4 | 1 | 14 | 2 |
5 | 2 | 15 | 4 |
6 | 2 | 16 | 2 |
7 | 2 | 17 | 1 |
8 | 5 | 18 | 1 |
9 | 1 | 19 | 1 |
10 | 1 | 20 | 2 |
S. No | Edges | Edge density | S. No | Edges | Edge density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | (1, 2) | 0.0577 | 11 | (20, 12) | 0.0102 |
2 | (2, 8) | 0.0443 | 12 | (12, 16) | 0.0240 |
3 | (8, 4) | 0.0754 | 13 | (16, 13) | 0.1428 |
4 | (8, 9) | 0.2558 | 14 | (13, 15) | 0.3405 |
5 | (8, 3) | 0.3401 | 15 | (15, 19) | 0.0128 |
6 | (8, 5) | 0.4822 | 16 | (15, 18) | 0.0248 |
7 | (5, 14) | 0.1238 | 17 | (15, 11) | 0.1084 |
8 | (14, 6) | 0.1534 | 18 | (11, 10) | 0.1100 |
9 | (6, 7) | 0.1078 | 19 | (11, 17) | 0.5513 |
10 | (7, 20) | 0.0272 |
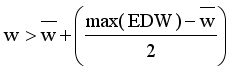 in the MST to generate subtree (clusters). Table 4, the longest edge weight 0.5513 connecting the data points 11 and 17 is find to be inconsistent one. By removing the inconsistent edge from the weighted LINEX HELLINGER_MST, data points partitioned into two subtrees or clusters
in the MST to generate subtree (clusters). Table 4, the longest edge weight 0.5513 connecting the data points 11 and 17 is find to be inconsistent one. By removing the inconsistent edge from the weighted LINEX HELLINGER_MST, data points partitioned into two subtrees or clusters 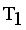 and
and 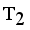 namely.
namely. 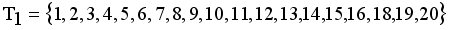 and
and 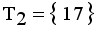 . Now minimal spanning tree produced outlier is {17}. Next to find minimum and maximum standard deviation of
. Now minimal spanning tree produced outlier is {17}. Next to find minimum and maximum standard deviation of 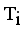 then Cluster Separation value less than 0.5625 is valid. Secondly to remove next longest edge, weighted LINEX HELLINGER distance based MST partitioned into Three subtrees or clusters
then Cluster Separation value less than 0.5625 is valid. Secondly to remove next longest edge, weighted LINEX HELLINGER distance based MST partitioned into Three subtrees or clusters 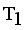 ,
, 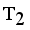 and
and 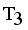 namely
namely 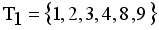 ,
, 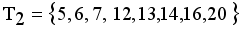 and
and 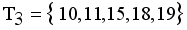 . Next to find minimum and maximum edge and to calculate standard deviation of
. Next to find minimum and maximum edge and to calculate standard deviation of 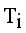 then Cluster separation value less than 0.5625 is valid. Here standard deviation of edge density
then Cluster separation value less than 0.5625 is valid. Here standard deviation of edge density 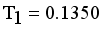 , Standard deviation of edge density
, Standard deviation of edge density 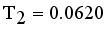 and Standard deviation of edge density
and Standard deviation of edge density 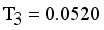 then
then 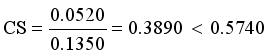 then we stop the removing inconsistent edges.. Finally minimal spanning tree produced three cluster center and 1 outliers. Then the center of the cluster and its convergence of standard FCM and LINEX HELLINGER distance based IFCM are determined under successive interations of experiments using data points. With the new efficient objective function based LINEX Hellinger distance induced weighted measure the termination value is achieved, with very less iteration and with much better performance in getting membership (Table 6) than standard FCM. Table 7 gives the number of iteration to achieve the results of cluster on the data points by standard FCM and weighted LINEX_IFCM. It is clear from the final cluster, membership (Table 6), scatter diagram (Figure 1), minimal spanning tree (Figure 2) that our proposed LINEX Hellinger _IFCM induced weighted degree of minimal spanning tree is much faster than the standard FCM and the method is converged fast to terminate condition with less run time. To test the effectiveness of weighted LINEX_IFCM, the edge density minimal spanning tree based IFCM is used as center. This is done to find out the fuzzy membership and appropriate number of clusters. Thus, we have concluded the final optimal clusters formed as 3 (Figure 3). This algorithm has also reduced the number of iterations. Best result is achieved by this measure fuzzy partition coefficient
then we stop the removing inconsistent edges.. Finally minimal spanning tree produced three cluster center and 1 outliers. Then the center of the cluster and its convergence of standard FCM and LINEX HELLINGER distance based IFCM are determined under successive interations of experiments using data points. With the new efficient objective function based LINEX Hellinger distance induced weighted measure the termination value is achieved, with very less iteration and with much better performance in getting membership (Table 6) than standard FCM. Table 7 gives the number of iteration to achieve the results of cluster on the data points by standard FCM and weighted LINEX_IFCM. It is clear from the final cluster, membership (Table 6), scatter diagram (Figure 1), minimal spanning tree (Figure 2) that our proposed LINEX Hellinger _IFCM induced weighted degree of minimal spanning tree is much faster than the standard FCM and the method is converged fast to terminate condition with less run time. To test the effectiveness of weighted LINEX_IFCM, the edge density minimal spanning tree based IFCM is used as center. This is done to find out the fuzzy membership and appropriate number of clusters. Thus, we have concluded the final optimal clusters formed as 3 (Figure 3). This algorithm has also reduced the number of iterations. Best result is achieved by this measure fuzzy partition coefficient 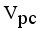 maximum and validation function
maximum and validation function 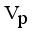 minimum (Table 8). The weighted LINEX_IFCM clustering algorithm has the following membership value intimacy (Table 6).
minimum (Table 8). The weighted LINEX_IFCM clustering algorithm has the following membership value intimacy (Table 6). Co-ordinate (x, y) | intensity | appropriate cluster | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
S. No | x | y | I (v) | Mem-1 | Mem-2 | Mem-3 | |
1 | 2.50 | 3.00 | 0.75 | 1 | 0.9213 | 0.0523 | 0.0265 |
2 | 3.80 | 3.50 | 0.50 | 2 | 0.9895 | 0.0072 | 0.0032 |
3 | 7.00 | 1.80 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.7820 | 0.1444 | 0.0736 |
4 | 3.10 | 4.80 | 0.18 | 1 | 0.8808 | 0.0830 | 0.0362 |
5 | 5.50 | 7.50 | 0.45 | 2 | 0.4630 | 0.4292 | 0.1077 |
6 | 8.50 | 9.50 | 0.75 | 2 | 0.0794 | 0.8548 | 0.0658 |
7 | 10.80 | 11.50 | 0.60 | 2 | 0.0046 | 0.9858 | 0.0096 |
8 | 4.20 | 3.80 | 0.25 | 5 | 0.9710 | 0.0202 | 0.0087 |
9 | 2.80 | 1.80 | 0.45 | 1 | 0.9149 | 0.0551 | 0.0299 |
10 | 12.50 | 20.50 | 0.65 | 1 | 0.0559 | 0.2632 | 0.6809 |
11 | 15.80 | 20.50 | 0.25 | 3 | 0.0199 | 0.0788 | 0.9013 |
12 | 11.80 | 12.50 | 0.35 | 2 | 0.0269 | 0.8865 | 0.0866 |
13 | 15.50 | 14.50 | 0.80 | 2 | 0.0480 | 0.3319 | 0.6201 |
14 | 5.50 | 10.50 | 0.70 | 2 | 0.2367 | 0.6315 | 0.1318 |
15 | 18.50 | 19.50 | 0.40 | 4 | 0.0026 | 0.0093 | 0.9882 |
16 | 12.50 | 13.80 | 0.25 | 2 | 0.0490 | 0.7068 | 0.2442 |
17 | 21.80 | 12.50 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.0852 | 0.2753 | 0.6395 |
18 | 19.80 | 20.50 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.0161 | 0.0513 | 0.9326 |
19 | 19.00 | 20.00 | 0.60 | 1 | 0.0050 | 0.0171 | 0.9779 |
20 | 11.00 | 12.00 | 0.30 | 2 | 0.0171 | 0.9420 | 0.0410 |
No. of iterations | No. of clusters | |
|---|---|---|
FCM | 11 | 3 |
KFCM | 8 | 3 |
Edge density MST initialization method based LINEX Hellingerdistance based Intuitionistic FCM | 3 | 3 |
Vpc | Vp | |
|---|---|---|
FCM | 0.8325 | 0.1825 |
KFCM | 0.8238 | 0.1720 |
MST initialization method based LINEX Hellinger Intuitionistic FCM | 0.8889 | 0.0661 |
| [1] | Atanassov KT, “Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Systems”, vol. 20, pp. 87-96 (1986). |
| [2] | Arora J and Tushir M,“Robust spatial intuitionistic fuzzy C-means with city-block distance clustering for image segmentation” Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, vol. 35, pp. 5255-5264 (2018). |
| [3] | Chaira T, “A novel intuitionistic fuzzy c means clustering algorithm and its application to medical images” Applied Soft computing, vol. 11(2), pp. 1711-1717 (2011). |
| [4] | Cheng D, Zhu Q, Huang J, Wu Q, and Yang L, ‘Clustering with local density peaks-based minimum spanning tree’, IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, vol. 33(2), pp. 374–387 (2021). |
| [5] | Jun Kong, Jian Hou, Min Jiang & Jinhua Sun, ‘‘A Novel Image Segmentation Method Based on Improved Intuitionistic Fuzzy C-Means Clustering Algorithm’, KSII transactions on internet and information systems, vol. 13(6), pp. 3121-3143 (2019). |
| [6] | Li G, Long C, Chen CLP and Zhou J, “Integrating guided filter into fuzzy clustering for noisy image segmentation” Digit. Signal Process, vol. 83, pp. 235–248 (2018). |
| [7] | Lohani QMD, Solanki R and Muhuri PK, ‘Novel adaptive clustering algorithms based on a probabilistic similarity measure over Atanassov intuitionistic fuzzy set’, IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., vol. 26(6), pp. 3715–3729 (2018). |
| [8] | Nithya M et al., “A Fiedler’s approach to LINEX Intuitionistic fuzzy c means clustering induced spectral initialization for data analysis”, Applied and Computational Mathematics, vol. 12 (4), pp. 82-91(2023). |
| [9] | Pop PC, ‘The generalized minimum spanning tree problem: an overview of formulations, solution procedures and latest advances’, European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 283(1), pp. 1–15 (2020). |
| [10] | Szmidt E and Kacprzyk J, “Distances between intuitionistic fuzzy sets” Fuzzy sets Systems, vol. 114, pp. 505-518(2000). |
| [11] |
Senthil S et al., “Efficient kernel induced fuzzy c-means based on Gaussian function for image data analyzing”, Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems,
https://doi.org/10.3233 , IFS-151820 IOS Press, 13 October 13. (2015). |
| [12] | Xu Z and Wu J, “Intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithms” J. Syst. Eng. Electron, vol. 21, pp. 580–590 (2010). |
| [13] | Zhao F, Chen Y, Liu H and Fan J, ‘Alternate PSO-based adaptive interval type-2 intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for color image segmentation’, IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 64028–64039 (2019). |
| [14] | Zhao F, Liu HQ, Fan JL, Chen CW, Lan R & N. Li N, ‘Intuitionistic fuzzy set approach to multi-objective evolutionary clustering with multiple spatial information for image segmentation’, Neurocomputing, vol. 312, pp. 296-309 (2018). |
| [15] | Xie X. L and Beni G, A validity measure for fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., Vol. 3(8), pp-841-847(1991). |
| [16] | Bezdek J. C., Hall L. O., Clarke L. P, Review of MR image segmentation techniques using pattern recognition, medical physics 20(4), pp. 1033-1048 (1993). |
| [17] | Rudolf Beran, Minimum Hellinger distance estimates for parametric models, University of California, Berkeley, The Annals of Statistics, Vol. 5(3), pp. 445-463 (1977). |
APA Style
M., N., Balasubramaium, K. B., S., S. (2024). MST Initialization Based Intuitionistic Fuzzy c Means Clustering Using LINEX Hellinger Distance and Its Applications. Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 12(2), 36-47. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.jeee.20241202.12
ACS Style
M., N.; Balasubramaium, K. B.; S., S. MST Initialization Based Intuitionistic Fuzzy c Means Clustering Using LINEX Hellinger Distance and Its Applications. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2024, 12(2), 36-47. doi: 10.11648/j.jeee.20241202.12
AMA Style
M. N, Balasubramaium KB, S. S. MST Initialization Based Intuitionistic Fuzzy c Means Clustering Using LINEX Hellinger Distance and Its Applications. J Electr Electron Eng. 2024;12(2):36-47. doi: 10.11648/j.jeee.20241202.12
@article{10.11648/j.jeee.20241202.12,
author = {Nithya M. and K. Bhuvaneswari Balasubramaium and Senthil S.},
title = {MST Initialization Based Intuitionistic Fuzzy c Means Clustering Using LINEX Hellinger Distance and Its Applications
},
journal = {Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering},
volume = {12},
number = {2},
pages = {36-47},
doi = {10.11648/j.jeee.20241202.12},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.jeee.20241202.12},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.jeee.20241202.12},
abstract = {Due to the uncertainty and fuzziness of information, the traditional clustering analysis method sometimes cannot meet the requirement in practice. The clustering method based on intuitionistic fuzzy set has attracted more and more scholars attention nowadays. This paper discusses the intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm. There are a number of clustering techniques developed in the past using different distance/similarity measure. In this paper, we proposed a improved edge density minimal spanning tree initilization method using LINEX hellinger distance based weighted LINEX intuitionistic fuzzy c means clustering. IFCM considered an uncertainty parameter called hesitation degree and incorporated a new objective function which is based upon intutionistic fuzzy entropy in the conventional Fuzzy C-means. The clustering algorithm has membership and non membership degrees as intervals. Information regarding membership and typicality degrees of samples to all clusters is given by algorithm. Furthermore, the algorithm is extended for calculating membership and updating prototypes by minimizing the new objective function of weighted LINEX intuitionistic fuzzy c-means. Finally, the developed algorithms are illustrated through conducting experiments on random dataset, partition coefficient and validation function are used to evaluate the validity of clustering also this paper compares the results of proposed method with the results of existing basic intuitionistic fuzzy c-means.
},
year = {2024}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - MST Initialization Based Intuitionistic Fuzzy c Means Clustering Using LINEX Hellinger Distance and Its Applications AU - Nithya M. AU - K. Bhuvaneswari Balasubramaium AU - Senthil S. Y1 - 2024/08/27 PY - 2024 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.jeee.20241202.12 DO - 10.11648/j.jeee.20241202.12 T2 - Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering JF - Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering JO - Journal of Electrical and Electronic Engineering SP - 36 EP - 47 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2329-1605 UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.jeee.20241202.12 AB - Due to the uncertainty and fuzziness of information, the traditional clustering analysis method sometimes cannot meet the requirement in practice. The clustering method based on intuitionistic fuzzy set has attracted more and more scholars attention nowadays. This paper discusses the intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm. There are a number of clustering techniques developed in the past using different distance/similarity measure. In this paper, we proposed a improved edge density minimal spanning tree initilization method using LINEX hellinger distance based weighted LINEX intuitionistic fuzzy c means clustering. IFCM considered an uncertainty parameter called hesitation degree and incorporated a new objective function which is based upon intutionistic fuzzy entropy in the conventional Fuzzy C-means. The clustering algorithm has membership and non membership degrees as intervals. Information regarding membership and typicality degrees of samples to all clusters is given by algorithm. Furthermore, the algorithm is extended for calculating membership and updating prototypes by minimizing the new objective function of weighted LINEX intuitionistic fuzzy c-means. Finally, the developed algorithms are illustrated through conducting experiments on random dataset, partition coefficient and validation function are used to evaluate the validity of clustering also this paper compares the results of proposed method with the results of existing basic intuitionistic fuzzy c-means. VL - 12 IS - 2 ER -