Designing compounds with high energetic performance and low sensitivity at the molecular level is the central challenge in molecular design for energetic materials. Molecular frameworks integrating 1,2,4-triazolo [4,3-b] [1,2,4,5] tetrazine (known as high-energy-density and low-sensitivity module) and monocyclic tetrazoles are constructed to design energetic compounds. A series of energetic compounds are constructed. Density functional theory (DFT) has been used to investigate geometries, frontier molecular orbital energy, heats of formation (HOFs), densities of the title compounds at B3PW91/6-31G (d, f) level. Heats of formation were calculated via isodesmic reactions. Crystal densities were predicted using Politzer's method. Detonation velocity (D) and detonation pressure (P) of the title compounds have been determined based on HOFs and densities through the Kamlet-Jacobs (K-J) equation. The effects of substituents on above properties are presented. Substitution with -NO2, -ONO2, -NH2, -NHNO2, and -N(NO2)2 groups can increase the heats of formation, densities, detonation velocity and detonation pressure of the compounds. Specifically, the compound substituted with the -N(NO2)2 group exhibits higher detonation performance than the high-energy explosive RDX, suggesting its potential as a promising high energy material. The results are of significant value, providing theoretical guidance for the molecular design of novel high-energy-density compounds and the optimization of established ones.
| Published in | Modern Chemistry (Volume 13, Issue 2) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.mc.20251302.12 |
| Page(s) | 40-47 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Science Publishing Group |
1,2,4-triazolo [4,3-b][1,2,4,5] Tetrazine, Density Functional Theory, Heats of Formation, Detonation Velocity, Detonation Pressure
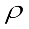 (g cm-3) of our study derivatives with consideration of the intermolecular interactions.
(g cm-3) of our study derivatives with consideration of the intermolecular interactions. 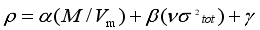 (1)
(1) 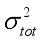 represents the variability measure of the electrostatic potential. α, β and γ are the coefficients assigned through fitting eq (1) to the experimental densities of a range of 36 energetic compounds. They are 0.9183, 0.0028, and 0.0443, respectively
represents the variability measure of the electrostatic potential. α, β and γ are the coefficients assigned through fitting eq (1) to the experimental densities of a range of 36 energetic compounds. They are 0.9183, 0.0028, and 0.0443, respectively 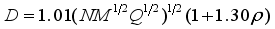 (2)
(2) 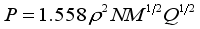 (3)
(3) Compd. | Compd. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
[1,2,4] triazolo[4,3-b]-[1,2,4,5] Tetrazine | 683.16 a | 2H-tetrazole | 327.35 a |
CH4 | -74.6 ± 0.3 b | NH2ONO2 | 29.90 a |
C6H6 | 82.9 ± 0.9 b | NH2OCH3 | -31.33 a |
NH3 | -45.9 b | NH2CN | 138.41 a |
CH3NHCH3 | -19.0 ± 2.0 b | NH2N3 | 421.12 a |
NH2NO2 | -2.38 a | NH2NHNO2 | 99.11 a |
NH2CH3 | -23.5 a | NH2N(NO2)2 | 181.80 a |
NH2NH2 | 95.35 a |
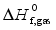 are the gas phase heat of formation in kJ mol-1.
are the gas phase heat of formation in kJ mol-1. 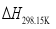 at 298.15K can be calculated through the reaction enthalpies:
at 298.15K can be calculated through the reaction enthalpies: 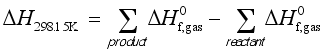 (4)
(4) 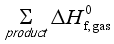 and
and 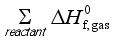 are the sums of the heats of formation for products and reactants in gas at 298.15K, respectively. Since the HOFs of reference compounds are available as shown in Table 1, the HOFs of the title compounds can be obtained if the heats of reaction
are the sums of the heats of formation for products and reactants in gas at 298.15K, respectively. Since the HOFs of reference compounds are available as shown in Table 1, the HOFs of the title compounds can be obtained if the heats of reaction 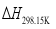 are known. The
are known. The 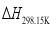 can be calculated from the following equations:
can be calculated from the following equations: 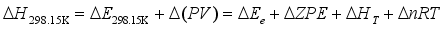 (5)
(5) Compd. | isodesmic work Reactions |
|---|---|
T0 | T0+2CH4→[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine+2H-tetrazole + CH3NHCH3 |
T1 | T1+NH3+2CH4→[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine+2H-tetrazole +NH2NO2+CH3NHCH3 |
T2 | T2+NH3+2CH4→[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine+2H-tetrazole +NH2ONO2+CH3NHCH3 |
T3 | T3+NH3+2CH4→[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine+2H-tetrazole +NH2CH3+CH3NHCH3 |
T4 | T4+NH3+2CH4→[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine+2H-tetrazole +NH2OCH3+CH3NHCH3 |
T5 | T5+NH3+2CH4→[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine+2H-tetrazole +NH2CN+CH3NHCH3 |
T6 | T6+NH3+2CH4→[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine+2H-tetrazole +NH2N3+CH3NHCH3 |
T7 | T7+NH3+2CH4→[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine+2H-tetrazole +NH2NH2+CH3NHCH3 |
T8 | T8+NH3+2CH4→[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine+2H-tetrazole +NH2NHNO2+CH3NHCH3 |
T9 | T9+NH3+2CH4→[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4,5]tetrazine+2H-tetrazole +NH2N(NO2)2+CH3NHCH3 |
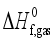 and the heat of sublimation enthalpy
and the heat of sublimation enthalpy 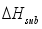 as,
as, 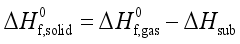 (6)
(6) 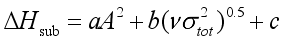 (7)
(7) 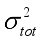 are defined and provided in the density calculation methodology (Section 2.2). a, b, and c are the coefficients optimized via iterative least-squares minimization. They were determined by the Byrd and Rice method
are defined and provided in the density calculation methodology (Section 2.2). a, b, and c are the coefficients optimized via iterative least-squares minimization. They were determined by the Byrd and Rice method 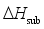 ) and gas/solid phase heats of formation (
) and gas/solid phase heats of formation ( 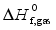 and
and 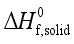 ) of the title compounds are listed in Table 3.
) of the title compounds are listed in Table 3. Compd. | E0 | ZPE | HT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
T0 | -756.0581 | 0.1151 | 29.31 | 994.45 | 27.22 | 880.55 |
T1 | -960.4292 | 0.1159 | 36.33 | 1119.90 | 28.84 | 999.24 |
T2 | -1035.5703 | 0.1198 | 39.10 | 1089.05 | 31.02 | 959.26 |
T3 | -795.3635 | 0.1429 | 33.75 | 976.92 | 27.74 | 860.87 |
T4 | -870.4824 | 0.1465 | 36.53 | 998.76 | 29.10 | 877.02 |
T5 | -848.2194 | 0.1122 | 34.01 | 1249.21 | 28.36 | 1130.55 |
T6 | -919.5298 | 0.1167 | 36.67 | 1473.05 | 29.52 | 1349.54 |
T7 | -811.3607 | 0.1315 | 33.44 | 1091.91 | 29.00 | 970.57 |
T8 | -1015.7535 | 0.1337 | 38.89 | 1173.36 | 31.52 | 1041.49 |
T9 | -1220.1198 | 0.1339 | 46.50 | 1283.89 | 34.89 | 1137.92 |
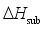 and HOF are in kJ mol-1.
and HOF are in kJ mol-1. Compd. | D | P | Is | ΔE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
T0 | 1.799 | 7.490 | 24.875 | 0.868 | 3.82 |
T1 | 1.840 | 8.291 | 30.896 | 0.947 | 3.95 |
T2 | 1.867 | 8.552 | 33.147 | 0.960 | 3.86 |
T3 | 1.677 | 6.919 | 20.335 | 0.852 | 3.73 |
T4 | 1.703 | 7.351 | 23.173 | 0.897 | 3.76 |
T5 | 1.751 | 7.371 | 23.702 | 0.909 | 3.97 |
T6 | 1.779 | 7.973 | 27.999 | 0.957 | 3.64 |
T7 | 1.781 | 7.610 | 25.522 | 0.886 | 3.65 |
T8 | 1.838 | 8.328 | 31.149 | 0.943 | 3.92 |
T9 | 1.901 | 8.927 | 36.504 | 0.984 | 3.96 |
DFT | Density Functional Theory |
HOF | Heat of Formation |
D | Detonation Velocity |
P | Detonation Pressure |
HOMO | Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital |
LUMO | Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital |
| [1] | Tang, J., Yang, P. J., Yang, H. W., Xiong, H. L., Hu, W., Cheng, G. B. A Simple and Efficient Method to Synthesize High-nitrogen Compounds: Incorporation of Tetrazole Derivatives with N5 chains, Chemical Engineering Journal. 2020, 386(124027) 1-13. |
| [2] | Fan, H. H., Tang, J., Hu, W., Zheng, X. X., Yang, P. J., Cheng, G. B., Xiao, C., Yang, H. W., Combination of Tetrazole and 4-Azido-pyrazolotriazine Oxide: Balance of High Nitrogen, Energy, and Safety, Organic Letter, 2025, 27(3) 846-850. |
| [3] | Chen, B. H, Lu, H., Chen, J. Y., Chen, Z. X., Yin, S. F., Peng, L. F., Qiu, R. H. Recent Progress on Nitrogen-Rich Energetic Materials Based on Tetrazole Skeleton. Topics in Current Chemistry, 2023, 381(5), 2365-0869. |
| [4] | Cui, Z. Y., Wang, J. H., Wu, L. L., Yuan, X., Yu, Q., Zhang, J. Lin, K. F., Yang, Y. L., Xia, D. B., Strategy for Balance Energy and Safety: Salt Formation of Nitrogen-Rich Bicyclic Compounds Based on 1,2,4-Triazole, Crystal Growth & Design, 2025, 25(1), 88-100. |
| [5] | Hu, L., He, C, L., Zhao, G., Imler, G. H., Parrish, D. A., Shreeve, J. M. Selecting Suitable Substituents for Energetic Materials Based on a Fused Triazolo-[1,2,4,5]tetrazine Ring, ACS Applied Energy Materials. 2020, 3(6), 5510-5516. |
| [6] | Liu, Y., Zhao, G., Tang, Y., Zhang, J., Hu, L., Imler, G. H., Parrish, D. A., Shreeve, J. M. Multipurpose [1,2,4] Triazolo[4,3-b] [1,2,4,5] Tetrazine-based Energetic Materials, Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 2019, 7(13), 7875-7884. |
| [7] | Frisch, M. J., Trucks, G. W., Schlegel, H. B., et al. Gaussian 09, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009. |
| [8] | Hahre, W. J., Radom, L., Schleyer, P. V. R. Ab initio molecular orbital theory, New York: Wiley; 1986. |
| [9] | Politzer, P., Martinez, J., Murray, J. S., Concha, M. C., Toro-Labbé, A. An Electrostatic Interaction Correction for Improved crystal Density Prediction, Molecular Physics, 2009, 107(19) 2095–2101. |
| [10] | Lu, T., Chen, F. W. Multiwfn: A Multifunctional Wavefunc- tion Analyzer, Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2012, 33(5), 580-592. |
| [11] | Kamlet, M. J., Jacobs, S. J. Chemistry of detonations. I. A Simple Method for Calculating Detonation Properties of C–H–N–O Explosives, Journal of Chemical Physics. 1968, 48(1), 23–35. |
| [12] | NIST Chemistry WebBook; Linstrom, P. J., Mallard, W. G., Eds.; NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69; National Institute Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg MD, 2005. |
| [13] | Byrd, E. F. C., Rice, B. M. Improved Prediction of Heats of For- mation of Energetic Materials Using Quantum Mechanical Calculations, Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 2006, 110(3), 1005–1013. |
| [14] | Xu, X. J., Zhu, W. H., Xiao, H. M. DFT Studies on the Four Polymorphs of Crystalline CL-20 and the Influences of Hydrostatic Pressure on Epsilon-CL-20 Crystal, Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 2007, 111(8) 2090-2097. |
APA Style
Su, X. (2025). Theoretical Investigation of Compounds Based on 1, 2, 4-Triazolo [4, 3-b] [1,2,4,5] Tetrazine as High Energy and Low Sensitivity Energetic Materials. Modern Chemistry, 13(2), 40-47. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.mc.20251302.12
ACS Style
Su, X. Theoretical Investigation of Compounds Based on 1, 2, 4-Triazolo [4, 3-b] [1,2,4,5] Tetrazine as High Energy and Low Sensitivity Energetic Materials. Mod. Chem. 2025, 13(2), 40-47. doi: 10.11648/j.mc.20251302.12
AMA Style
Su X. Theoretical Investigation of Compounds Based on 1, 2, 4-Triazolo [4, 3-b] [1,2,4,5] Tetrazine as High Energy and Low Sensitivity Energetic Materials. Mod Chem. 2025;13(2):40-47. doi: 10.11648/j.mc.20251302.12
@article{10.11648/j.mc.20251302.12,
author = {Xinfang Su},
title = {Theoretical Investigation of Compounds Based on 1, 2, 4-Triazolo [4, 3-b] [1,2,4,5] Tetrazine as High Energy and Low Sensitivity Energetic Materials
},
journal = {Modern Chemistry},
volume = {13},
number = {2},
pages = {40-47},
doi = {10.11648/j.mc.20251302.12},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.mc.20251302.12},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.mc.20251302.12},
abstract = {Designing compounds with high energetic performance and low sensitivity at the molecular level is the central challenge in molecular design for energetic materials. Molecular frameworks integrating 1,2,4-triazolo [4,3-b] [1,2,4,5] tetrazine (known as high-energy-density and low-sensitivity module) and monocyclic tetrazoles are constructed to design energetic compounds. A series of energetic compounds are constructed. Density functional theory (DFT) has been used to investigate geometries, frontier molecular orbital energy, heats of formation (HOFs), densities of the title compounds at B3PW91/6-31G (d, f) level. Heats of formation were calculated via isodesmic reactions. Crystal densities were predicted using Politzer's method. Detonation velocity (D) and detonation pressure (P) of the title compounds have been determined based on HOFs and densities through the Kamlet-Jacobs (K-J) equation. The effects of substituents on above properties are presented. Substitution with -NO2, -ONO2, -NH2, -NHNO2, and -N(NO2)2 groups can increase the heats of formation, densities, detonation velocity and detonation pressure of the compounds. Specifically, the compound substituted with the -N(NO2)2 group exhibits higher detonation performance than the high-energy explosive RDX, suggesting its potential as a promising high energy material. The results are of significant value, providing theoretical guidance for the molecular design of novel high-energy-density compounds and the optimization of established ones.
},
year = {2025}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - Theoretical Investigation of Compounds Based on 1, 2, 4-Triazolo [4, 3-b] [1,2,4,5] Tetrazine as High Energy and Low Sensitivity Energetic Materials AU - Xinfang Su Y1 - 2025/06/26 PY - 2025 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.mc.20251302.12 DO - 10.11648/j.mc.20251302.12 T2 - Modern Chemistry JF - Modern Chemistry JO - Modern Chemistry SP - 40 EP - 47 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2329-180X UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.mc.20251302.12 AB - Designing compounds with high energetic performance and low sensitivity at the molecular level is the central challenge in molecular design for energetic materials. Molecular frameworks integrating 1,2,4-triazolo [4,3-b] [1,2,4,5] tetrazine (known as high-energy-density and low-sensitivity module) and monocyclic tetrazoles are constructed to design energetic compounds. A series of energetic compounds are constructed. Density functional theory (DFT) has been used to investigate geometries, frontier molecular orbital energy, heats of formation (HOFs), densities of the title compounds at B3PW91/6-31G (d, f) level. Heats of formation were calculated via isodesmic reactions. Crystal densities were predicted using Politzer's method. Detonation velocity (D) and detonation pressure (P) of the title compounds have been determined based on HOFs and densities through the Kamlet-Jacobs (K-J) equation. The effects of substituents on above properties are presented. Substitution with -NO2, -ONO2, -NH2, -NHNO2, and -N(NO2)2 groups can increase the heats of formation, densities, detonation velocity and detonation pressure of the compounds. Specifically, the compound substituted with the -N(NO2)2 group exhibits higher detonation performance than the high-energy explosive RDX, suggesting its potential as a promising high energy material. The results are of significant value, providing theoretical guidance for the molecular design of novel high-energy-density compounds and the optimization of established ones. VL - 13 IS - 2 ER -